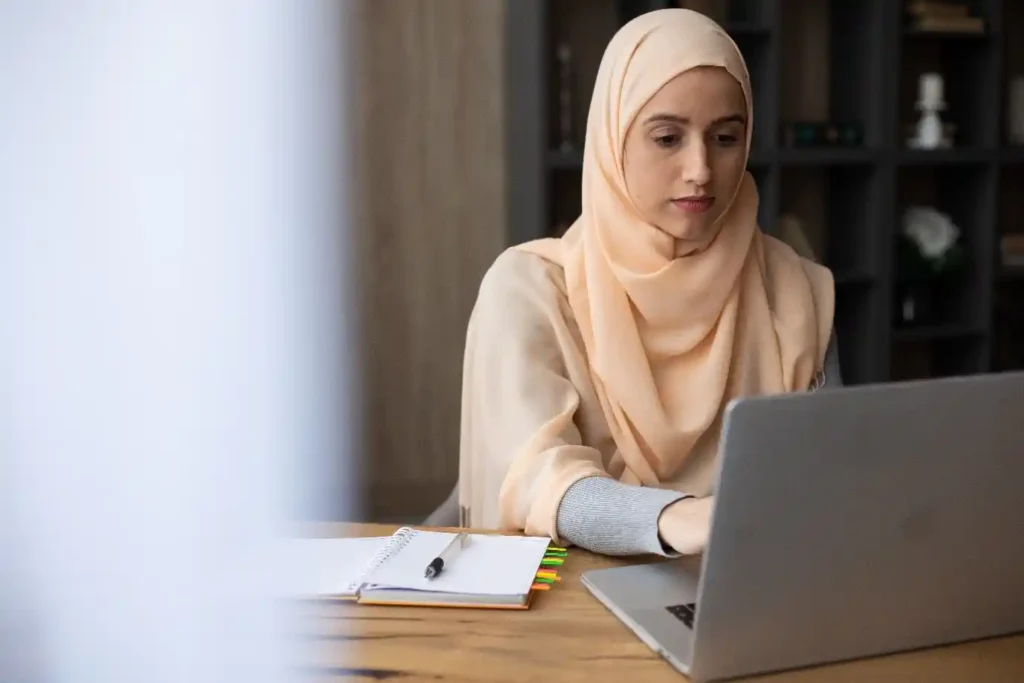
An Human Resource Management System (HRMS), is a suite of software applications used to manage human resources and related processes throughout the employee lifecycle. An HRMS enables a company to fully understand its workforce while staying compliant with changing tax laws and labor regulations.
Basically a digital personal assistant to do tedious work for HR professionals. An HRMS helps manage employee functions like calculating and communicating time-off, onboarding paperwork, and managing employee performance—which lets HR focus on more important, strategic work.
- What Is The Attendance Management System Dashboard?
- Why Human Resources Management Is So Important?
- Functions and Requirements For Human Resource Management System
- How Biometric Attendance and Payroll Management System Helps In Reducing HR Works?
- Is The HR System Important For Small Business Needs?
- How Much Does It Cost To Outsource Payroll?
- Are There Ways to Save on Outsourcing?
HR leaders and staff are the primary users, given that they run day-to-day workforce operations and are responsible for compliance and performance reporting. However, HR isn’t the only department that benefits. Companies can empower managers and employees with self-service for common tasks—an important selling point for younger hires. Executives can use an HRMS to generate data on workforce trends and their business implications.
And given that HR-related costs are some of the largest expenses incurred by a company, HRMS integration with the accounting system is invaluable for finance teams. Leading providers will go beyond basic accounting to help a company wring more financial insights out of HR data.
What’s the Difference between HRIS and HRMS?
So, what’s the difference between Human Resource Information System (HRIS) and Human Resource Management System (HRMS)? Most providers have combined the two systems and use the terms interchangeably since they work so closely together. Traditionally, an HRIS has been used to describe a system that tracks static employee information like social security number and name while an HRMS focuses more on the aspects of managing employee functions like performance, time off, and onboarding.
History of HRMS
In the 1970s, as companies looked to automate management of their people, payroll became the first HRMS function to be computerized. But it took mainframe technology to calculate a worker’s earnings, withhold deductions, print a paper check and track payroll liabilities. It wouldn’t be until the early 2000s, with widespread adoption of direct deposit and employee self-service, that the payroll process became wholly electronic.
The rise of the internet in the late 1990s brought the benefits of automation to even more HR processes. For example, paper-based help-wanted ads were replaced by electronic job boards, giving recruiters and candidates new ways to connect. By the 2010s, cloud technology was mainstream—now, HR teams at all-size companies could afford a suite of applications without investing in expensive computer hardware or IT staff to operate and maintain the system.

What Is The Attendance Management System Dashboard
The Attendance Management System Dashboard gives you a snapshot of when your employees and/or colleagues are present at your business office, home office, have a break or are absent. It allows you to easily create custom reports for the Finance office’s budgeting needs.
Employee attendance has always been a hot topic that business owners may care about. Through attendance data, you can get a general understanding of the basic performance of employees. At the same time, attendance is also an important standard for the salary base. For some companies, matters such as production and customer support require timely employee attendance. Low attendance rate is closely related to low employee success rate. The attendance dashboard & reporting system can strongly help you. (Read More)
Why HRMS Is Important?
A good HR department is critical to an employee-oriented, productive workplace in which employees are energized and engaged. Click here to find out the key reasons.
Functions of an HRMS
When considering which HRMS is right for your company, it’s helpful to think in terms of functional components. Generally, modern systems cover seven areas, with varying levels of focus.
Candidate management: Relates to employment offers to candidates and how you promote your brand to both the outside world and current employees who may wish to apply for internal jobs or make referrals. Critical for companies for which the candidate experience is a primary concern—from applying to resume management to interview scheduling to making offers, all the way through onboarding.
Employee engagement: People who are more engaged tend to produce higher-quality work and more fully adopt the company’s values and execute its vision, so how an employee connects with leadership and colleagues is important. Often, the HRMS is the route to complete a training course, acquire a new skill, develop a career path, gain recognition or become a mentor.
Employee management: There’s a reason this function is often referred to as “core HR.” Delivers a central portal to support analysis, reporting and compliance processes. It’s where you structure your workforce into organizational units, like departments or locations; define reporting relationships between managers and employees; and align payroll to accounting cost centers. It’s here where personal information is recorded and maintained, and this function is the cornerstone of efforts to offer employee self-service, maximize reporting and improve HR service delivery.
Optimization: Gleaning information from the HRMS to develop a vision for the future workforce is a primary selling point. It’s also the least-utilized function of a typical HRMS. The real value of this function usually comes to the fore with a merger or acquisition, sharp economic swings in either direction or when executives exit. Companies that take a proactive approach to optimizing the workforce are more resilient to change, have higher retention of top talent and better employee engagement.
Payroll: This is also a primary function of the HRMS—calculating earnings from gross to net or net to gross and withholding individual deductions and issuing payments can be made just as routine as paying the rent. Payroll functions comprise benefit elections and both employee and employer costs. Full-service payroll solutions also automate tax filing and deposits. Self-service functions allow employees to make changes to elective deductions, direct deposit accounts and tax withholdings and retrieve copies of earning statements without HR assistance.
Workforce management: This is where HR teams track employee development, manager evaluations and disciplinary actions; record time and attendance; and ensure the company is providing a healthy and safe work environment. This is also where compensation planning, performance management, learning and incident recording functions reside. HR can develop timesheet structures, overtime rules, time-off policies and approval chains in a way that maximizes automation, control and efficiency. The employee performance review process, complete with goal management, is set up in this function as well.
Contingent workforce management: Related to primary workforce management and critical for companies where not every employee is full-time. Contractors, consultants, interns and temporary employees provide specialized skills, support local community initiatives or university programs and handle spikes in demand for labor. The HRMS does not wholly manage these relationships because these employees are not always on the payroll and are usually not eligible for benefits; but the work they do contributes to company success, and it’s important to track how many contingent employees are on board at any given time and the total costs.
Once you have a clear understanding of which functions are most important, it’s time to dig into specific features.
What is a Biometric Attendance System?
Biometric Attendance Management System is the attendance system that employs ‘biometrics’ or biometric devices to register employee attendance and make the process of marking attendance as well as generating attendance reports easy.
Modern attendance systems are much more advanced than traditional systems, while also being much more efficient and effective. It also avoids all the pitfalls of earlier systems that were error-prone and hence, unreliable.
The cloud-based online management system lets your employees and managers tackle leave requests with ease. With the help of this system, your employees will be able to view their leave balance, holiday list and other records anytime from any device with a web browser.
The most important factor here is that the attendance management system does not require any new hardware for implementing it. You need not acquire any special biometric device for using the system. (Read More)
Is The HR System Important For Small Business Needs?
When you’re putting so much of yourself into your small business, it can be easy to think of HR as a line item or fixed cost with few variables—once the HR box has been checked, it’s time to move on to more important things. But as your small business grows into a medium-sized business, great HR can have an enormous positive impact on your bottom line, as long as you can keep up with the exponentially-increasing amount of time, thought, and effort it takes to respond to employees’ HR needs.
When done right, HR leads to a host of long-term benefits, including faster communication between employees, improved employee engagement, and more successful recruiting as your business gains a reputation for professionalism and competence. These benefits far outweigh the cost of moving on from DIY spreadsheet HR. (Read More)
How Much Does It Cost To Outsource Payroll?
As you can see, there are many factors that can impact the total cost of payroll processing. While the general rule of thumb is that it will cost around RM150-RM250 per employee per year, your total price will be based on the scope of your engagement with your vendor.
This is a relatively small price to pay compared to the risks of doing it yourself like errors, late payments, or compliance issues. In fact, with each pay run, you’re potentially costing your business more than what you’d pay for a provider.
Outsourcing your payroll comes with a lot to think about. Start your journey by learning which companies we consider to be the best regional and national payroll providers. If you think PeopleX is right for you, read more about our payroll packages to see which is a good fit for your business.
Are There Ways to Save on Outsourcing?
Since there’s so much variability in pricing, you may be wondering if there are ways you can save on payroll costs. The quest for less expensive options has fueled the rise in popularity of Do-It-Yourself (DIY) online payroll software. These DIY solutions can cost up to 50% less on a PEPM basis.
The reason for the savings is that you as the employer take on more responsibility in the payroll process such as employee maintenance, payroll detail entry and report production. These solutions are also paperless so by paying your employees with alternate methods such as direct deposit, you don’t incur costs for things like check delivery.
For many businesses, the DIY option can be an excellent way to save as long as you’re comfortable with web- or mobile-based systems and limited interaction with your provider. It’s also convenient if your payroll company’s hours of operation make it challenging for you to deal with them during normal business hours and you’d prefer to handle payroll before or after they are open.
But it’s also important to understand that there are some things you’ll be giving up with this approach. (Read More)